Orchestra,
ensemble of musical instruments; in the
narrowest sense, the characteristic ensemble of Western music, having as
its core a group of bowed stringed instruments of the
violin family, augmented by woodwind, brass, and percussion instruments. Orchestra
can also refer to various specialised ensembles, such as a balalaika orchestra, a
jazz orchestra, or
a gamelan (the tuned-percussion orchestra used in Indonesian Music). The word orchestra
originally signified the section in ancient Greek theatres between the stage and the
audience that was used by dancers and instrumentalists. In a modern theatre the part of
the auditorium reserved for musicians is called the orchestra pit.
Sections of the Orchestra
The string section, which
forms the backbone of orchestral sound, is divided into five parts: first violins, second
violins, violas, cellos, and double basses. The double
basses sometimes duplicate the cello part an octave lower, but often the music calls for
an independent bass part. The number of players in a modern orchestra can vary from about
two dozen or fewer to well over 100. Of these, the woodwind and brass sections each
constitute about 10 to 20 per cent of the orchestra, and the percussion about 10 per cent.
For the strings, certain proportions have proved to give the most effective balance of
sound; an orchestra with 20 first violins is likely to have about 18 to 20 second violins,
14 violas, 12 cellos, and 8 double basses; these numbers may vary, but they are considered
representative.
The woodwind and brass
sections, unlike the strings, normally have only one player per part. Until the mid-19th
century, the woodwind section consisted of two flutes, two oboes, two clarinets, and two
bassoons (a formation
known as double wind); the two members of each pair played different musical parts. By the
late 19th century three of each instrument was common (triple wind), with the third player
sometimes switching to a related instrument (for example, Cor Anglais, piccolo, double
bassoon, bass clarinet). The brass section, in its fully developed form, typically
consists of four horns, three trumpets, three trombones, and a tuba. These are
sometimes augmented by other brass instruments, such as the bass trombone or the Wagner
tuba designed by the German composer Richard Wagner and used in
his scores. The percussion section, in addition to one player who plays only the
timpani, has
traditionally emloyed one or two players, each of whom covers several instruments. The
basic percussion group up to the mid-19th century consisted of a side drum (snare drum),
a bass drum, cymbals, and a triangle. In the 20th
century, however, works employing ten or more players and dozens of different instruments
have become common, while the total number of percussion instruments in use has grown into
the hundreds. In addition to these four groups (bowed string, woodwind, brass, and
percussion), most orchestras also have a harp and a piano.
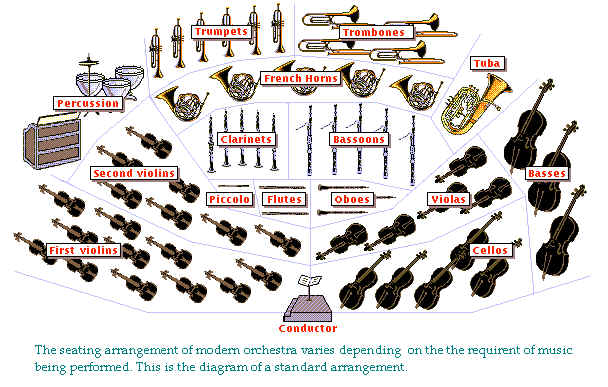
Seating Arrangement

The seating of the orchestra
is determined by the conductor, who directs
the orchestra in performance. The first and second violins are usually placed to the left
of the conductor, the violas, cellos, and basses to the right (a common variation is for
the first and second violins to face each other on opposite sides of the conductor). The
woodwind and brass are in front of the conductor but behind the strings, and the
percussion are placed farthest back.
Kinds of Orchestras
Opera and
ballet orchestras
share with symphony orchestras the size and structure described above; they differ in
their ancestry and function. The symphony orchestra performs symphonies, concertos, and
other concert music and is normally placed on a stage. Opera and ballet orchestras are
part of theatrical performances and are seated in the orchestra pit of a theatre (a space in
front of and partly underneath the stage). A chamber orchestra is one consisting usually
of 25 or fewer players. Virtually all orchestras before 1800 were of this size, and many
20th-century composers call for chamber orchestras. A string orchestra, which may be of
chamber-orchestra size or may be quite large, consists of the standard orchestral string
section, with no added wind or percussion instruments.
History